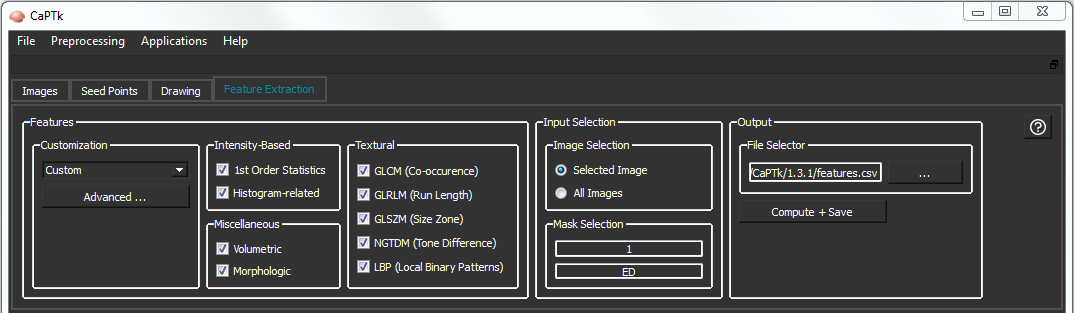
The feature extraction tab in CaPTk enables clinicians and other researchers to easily extract feature measurements, commonly used in image analysis, and conduct large-scale analyses in a repeatable manner. Although the feature panel in CaPTk is continuously expanding, it currently comprises i) intensity-based, ii) textural, and iii) volumetric/morphologic features.
The specialized applications in CaPTk, such as the EGFRvIII Surrogate Index, Survival Prediction, Recurrence Estimator, and SBRT-Lung use features of this panel. The general idea is to keep the features generic and adaptable for different types of medical images by just changing the input parameters. For now we provide some pre-selected parameters for Neuro and Torso images (i.e., Brain, Breast, Lung). Users can alter these pre-selected values through the Custom menu option, or create their own set of parameters via the Advanced menu. The output of the feature extraction tab can be either a .csv or an .xml file, with feature names and values. The table below gives details about the currently available features. Note that the reported features are extracted per modality, per annotated region and per offset (offset represents the radius around the center pixel; for radius 1, the offset will be +/- 1) value.
In the visualization panes, the "Z" axis is the center; and "Y" and "X" are to its left and right, respectively. "Z" represents the Axial view for RAI-to-LPS images.
| Feature Family | Specific Features | Parameter Name | Range | Default | Description, Formula and Comments |
| First Order Statistics |
| N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
|
| Histogram -based |
| Num_Bins | N.A. | 10 |
|
| Volumetric |
| Dimensions Axis | 2D:3D x,y,z | 3D z |
|
| Morphologic |
| Dimensions Axis | 2D:3D x,y,z | 3D z |
|
| Local Binary Pattern (LBP) | Radius Neighborhood | N.A. 2:4:8 | N.A. 8 |
| |
| Grey Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) |
| Num_Bins Num_Directions Radius Dimensions Offset Axis | N.A. 3:13 N.A. 2D:3D Average/Individual x,y,z | 10 13 2 3D Average z | For a given image, a Grey Level Cooccurrence Matrix is created and \( g(i,j) \) represents an element in matrix
|
| Grey Level Run-Length Matrix (GLRLM) |
| Num_Bins Num_Directions Radius Dimensions Axis Offset Distance_Range | N.A. 3:13 N.A. 2D:3D x,y,z Average/Individual 1:5 | 10 13 2 3D z Average 1 | For a given image, a run-length matrix \( P(i; j)\) is defined as the number of runs with pixels of gray level i and run length j.
|
| Neighborhood Grey-Tone Difference Matrix (NGTDM) |
| Num_Bins Num_Directions Dimensions Axis Distance_Range | N.A. 3:13 2D:3D x,y,z 1:5 | 10 13 3D N.A. 1 |
|
| Grey Level Size-Zone Matrix (GLSZM) |
| Num_Bins Num_Directions Radius Dimensions Axis Distance_Range | N.A. 3:13 N.A. 2D:3D x,y,z 1:5 | 10 13 2 3D z 4 | For a given image, a run-length matrix \( P(i; j)\) is defined as the number of runs with pixels of gray level i and run length j.
All features are estimated within the ROI in an image, considering 26-connected neighboring voxels in the 3D volume. |
REQUIREMENTS:
- An image or a set of co-registered images
- An ROI set containing masks of various labels, for which features will be extracted. If an ROI set is not provided, features can be calculated for the entire image.
USAGE:
- Load image(s) and an ROI set (if an ROI set is not available, the user can draw a mask using any label).
- Select the type of features to extract from the drop-down menu:
- SBRT_Lung: the feature definition provided by CBICA which have been used to generate features for SBRT_Lung
- Custom: manually selected & customized features
- Use the Advanced button to parameterize the selected features.
- Select the image to extract features from, or select
All Imagesunder the Image Selection dialog to extract features for all the images that have been loaded in CaPTk. - The user has the option to extract features only for specific labels included in the loaded ROI (default behavior is feature extraction for all labels). Number of request labels for feature extraction should match up with their respective names.
- Click on browse button and provide a location for the CSV (or XML) output file.
- Use the Advanced button to parameterize the selected features.
- Click compute.
- The results are saved in the specified file.
